Chemotherapy side effects are an important part of the treatment journey to understand, as they help patients prepare both physically and emotionally. Chemotherapy is a powerful cancer therapy designed to destroy fast-growing cancer cells, but it can also affect healthy cells, leading to a range of reactions. Recognizing these chemotherapy side effects early allows individuals to manage symptoms more effectively and stay in control of their health.
Understanding the Impact of Chemotherapy
When someone is diagnosed with cancer, chemotherapy is often a recommended course of treatment. However, many patients and their families are concerned about the side effects. Chemotherapy works by targeting rapidly dividing cells, which include not just cancer cells but also healthy ones. As a result, the treatment can lead to a wide range of side effects, impacting various parts of the body.
For anyone about to undergo chemotherapy or supporting a loved one, knowing what to expect from chemotherapy side effects can help you feel more in control and better prepared.
What Types of Cancer can Chemotherapy Treat?
Chemotherapy in cancer treatment is versatile and can treat a wide range of cancers, either alone or in combination with other therapies. It’s commonly used for cancers that spread rapidly, or for those that are hard to treat surgically. Some types of cancer chemotherapy can treat effectively include:
- Breast Cancer
- Leukemia
- Lung Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Colon Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
Chemotherapy may also be used to shrink tumors before surgery, common side effects from chemotherapy kill remaining cancer cells post-surgery, or treat cancer that has spread (metastasized).
Benefits of Chemotherapy?
Despite the challenges posed by chemotherapy treatment side effects, chemotherapy offers significant benefits in cancer care. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Targeting Cancer Cells: Chemotherapy is designed to target and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells, which helps shrink tumors and stop the spread of cancer.
- Adjunct to Other Treatments: Chemotherapy can be used in conjunction with surgery, radiation, or immunotherapy to enhance the effectiveness of the overall treatment plan.
- Prevent Recurrence: After surgery or radiation, chemotherapy can help kill any remaining cancer cells, lowering the chances of recurrence.
- Palliative Care: In some cases, chemotherapy can be used to manage symptoms, slow down cancer progression, and improve the quality of life, even when a cure is not possible.
Chemotherapy remains one of the most effective treatments for many types of cancer, despite the chemotherapy side effects that can occur during treatment.
Why Does Chemotherapy Cause Side Effects?
Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting and destroying fast-growing cancer cells. However, these drugs don’t differentiate between cancer cells and healthy cells. Healthy cells that also grow quickly such as those in your hair, digestive system, and bone marrow can also be affected, leading to chemotherapy treatment side effects.
Here’s why chemo causes side effects:
- Targeting fast-growing cells: Chemotherapy is designed to kill cells that grow rapidly, which includes cancer cells. Unfortunately, healthy cells in the body that divide quickly like those in hair follicles, the digestive system, and bone marrow can be impacted as well, causing chemo side effects on brain function, hair loss, fatigue, and more.
- Impact on normal tissues: Since chemotherapy doesn’t specifically target cancer cells, it can harm normal cells in areas like the stomach, intestines, mouth, and blood, which leads to a range of chemotherapy cancer treatment side effects.
- Immune system compromise: Chemo can suppress the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and other illnesses, adding to the list of chemotherapy treatment side effects.
Understanding the root cause helps explain why these side effects can vary from person to person.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Side Effects
Side effects during chemotherapy can range from mild to severe. While some symptoms are expected, others signal a need for urgent medical care. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Get immediate help if you notice :
- Fever exceeding 100.4°F (38°C)
- Continuous vomiting or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Easy bruising or bleeding without injury
- Disorientation or persistent headaches
- Pain that worsens despite medication
Infections and reduced immunity are major risks due to lowered white blood cells. If your body is unable to fight infection, something minor can quickly become serious. Keeping your care team informed ensures timely adjustments to medication or treatment plans.
Always trust your instincts if something feels wrong, contact your oncologist. Quick action can significantly reduce complications, helping you stay on track during your treatment. Your safety depends not only on medical therapies but also on your awareness and response to any unusual symptoms.
What to Expect During Your 1st Chemo Treatment Side Effects
The first chemo session can be daunting, as you may not know how your body will react. Each person’s experience is unique, but here are some of the 1st chemo treatment side effects you might encounter:
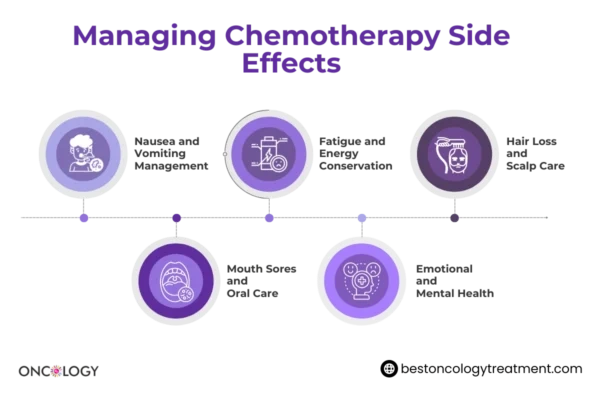
Fatigue:
Fatigue is one of the most common chemotherapy side effects and can significantly impact daily life. Many patients experience persistent tiredness during and after their treatment. This exhaustion is due to the impact chemo side effects on brain has on healthy cells, particularly in the bone marrow, which produces red blood cells.
Managing fatigue involves:
- Prioritizing rest
- Staying hydrated
- Engaging in light physical activities like walking
While fatigue can vary depending on the individual, understanding your body’s limits during the 1st chemo treatment side effects can help manage it more effectively.
Nausea and Vomiting:
Nausea and vomiting are frequent complaints among patients undergoing chemotherapy cancer treatment side effects. These chemotherapy side effects can occur immediately after treatment or even days later. The intensity can range from mild discomfort to severe vomiting.
To manage nausea and vomiting:
- Anti-nausea medications can be prescribed by your doctor.
- Eating smaller, frequent meals.
- Avoiding strong odors and greasy foods can help alleviate symptoms.
Patients often wonder, “What are the worst side effects of chemotherapy?” For many, nausea ranks high, but modern medicine has developed effective treatments to reduce its severity.
Hair Loss:
Hair loss, or alopecia, is one of the more visible chemotherapy side effects. Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cells, and since hair cells fall under this category, it is common to experience hair thinning or total loss.
While hair loss might occur on the scalp, it can also extend to eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair. Many patients find this part of the process emotionally challenging. chemotherapy in cancer Hair generally starts to regrow after the completion of chemotherapy.
Some tips for managing hair loss include:
- Wearing wigs, hats, or scarves.
- Using gentle shampoos and conditioners.
- Embracing your appearance and seeking support from loved ones or support groups.
Weakened Immune System:
Chemotherapy weakens the immune system by reducing white blood cells, which are crucial in fighting infections. This leaves patients more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.
To manage a weakened immune system:
- Avoid contact with sick individuals.
- Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing.
- Consult your doctor immediately if you develop a fever or signs of infection.
When considering chemotherapy side effects long-term, immune system suppression is something that may extend beyond the immediate treatment period, necessitating continued precautions.
Cognitive Changes (Chemo Brain):
Cognitive changes, often referred to as “chemo brain,” are common during and after chemotherapy. Patients report issues with memory, concentration, and multitasking, which can last for months or even years after treatment.
Ways to manage cognitive issues:
- Keeping a daily planner to stay organized.
- Engaging in brain exercises, such as puzzles or reading.
- Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
The question “At what stage of cancer is chemotherapy used?” often arises. Chemotherapy is used in various stages of cancer, from early to advanced, either to shrink tumors before surgery or radiation or to eliminate residual cancer cells after surgery. chemotherapy treatment side effects It can also be used in advanced cancers to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
What are the Worst Side Effects of Chemotherapy?
One of the most common questions patients have is, “What are the worst side effects of chemotherapy?” While everyone’s experience varies, certain side effects can be particularly challenging:
- Infection Risk: Chemotherapy weakens the immune system by reducing the number of white blood cells, making it easier to get infections. Therefore, it’s essential to be cautious, practice good hygiene, and avoid contact with sick people.
- Neuropathy: Tingling, numbness, or pain in the hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy) can be uncomfortable and affect daily activities.
- Mouth Sores: Some chemotherapy drugs can cause painful sores in the mouth, making it difficult to eat or speak.
- Cognitive Changes: Sometimes referred to as “chemo brain,” this side effect can involve memory problems, confusion, or difficulty concentrating.
While these side effects may sound daunting, many can be managed or mitigated with proper care. Always discuss your symptoms chemotherapy in cancer with your doctor so they can help find solutions.
Chemotherapy Side Effects Long-term
For some patients, chemotherapy side effects don’t end when the treatment stops. Chemotherapy side effects long-term can include:
- Heart and Lung Damage: Certain chemotherapy drugs may lead to long-term damage to the heart or lungs. Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor your health after treatment.
- Fertility Issues: Chemotherapy can affect fertility, particularly in younger patients. If this is a concern, discussing options like sperm banking or egg freezing before treatment is important.
- Bone Density Loss: Chemotherapy can affect bone health, leading to conditions like osteoporosis over time.
- Risk of Secondary Cancers: In rare cases, chemotherapy can increase the risk of developing a different type of cancer years later.
Understanding these potential long-term effects helps you monitor your health and take preventive actions, common side effects from chemotherapy like staying active, eating well, and having regular follow-up appointments with your oncologist.
At What Stage of Cancer is Chemotherapy Used?
Chemotherapy can be used at various stages of cancer, depending on the type and progression of the disease. It is commonly used:
- As Primary Treatment: For certain cancers, especially blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, chemotherapy is the main treatment.
- After Surgery (Adjuvant Therapy): To kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Before Surgery (Neoadjuvant Therapy): To shrink tumors and make surgery easier or more effective.
- For Advanced or Metastatic Cancer: In later stages, chemotherapy is often used to control the spread of cancer and improve quality of life, even if curing the cancer is no longer possible.
Your oncologist will explain the goals of chemotherapy in your treatment plan, based on the stage and type of cancer you’re facing.
Does Your Body Ever Fully Recover from Chemotherapy ?
Recovering from chemotherapy is a personal journey that varies by individual. While the body does work to heal after treatment, the speed and completeness of recovery depend on your age, overall health, type of cancer, and drugs used. Many patients regain full strength, though some may experience lingering effects.
Short-term side effects such as fatigue, digestive discomfort, or hair loss typically improve within weeks to months. However, certain issues like nerve damage, fertility problems, or cognitive fog may take longer or become long-term.
Helpful steps for recovery include
- Maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients
- Participating in light physical activity for energy restoration
- Getting consistent sleep and rest
- Attending follow-up visits with your care team
People often ask, “Is chemotherapy painful?” The procedure itself isn’t typically painful, but side effects like mouth ulcers, body aches, or nerve pain can cause significant discomfort. These are usually managed with medication.
Overall, the body is resilient. With proper care and monitoring, many patients return to regular routines and activities, though patience and ongoing support are key parts of the process.
How Long Do Side Effects from Chemotherapy Last?
The duration of chemotherapy side effects varies. Some people may experience mild, short-lived side effects, while others may encounter long-lasting or even permanent effects. chemotherapy treatment side effects Typically, most common side effects from chemotherapy, such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue, begin to subside a few weeks after completing the treatment. chemotherapy in cancer However, it’s essential to discuss with your oncologist to manage expectations and determine if side effects are temporary or persistent.
- Immediate Side Effects: Nausea, fatigue, and hair loss often appear within days of the first chemotherapy session.
- Short-Term Side Effects: Some, like fatigue and mouth sores, may last for weeks after chemotherapy ends.
- Long-Term Side Effects: For certain chemotherapy regimens, side effects such as nerve damage or fertility issues may be long-lasting.
Understanding the timeline of chemotherapy side effects can help patients manage their symptoms and prepare for their treatment journey.
Why is Follow-Up Care After Chemotherapy so Important?
Follow-up care is a crucial part of the recovery process after chemotherapy because it helps monitor healing, detect complications early, and ensure long-term health. Chemotherapy medicines continue to affect the body even after treatment ends, making regular evaluations essential to manage chemotherapy side effects and maintain overall well-being. These appointments allow healthcare providers to track physical changes, assess emotional health, and prevent long-term complications related to treatment.
Why Follow-Up Care Matters
- Monitors lingering chemotherapy treatment side effects: Many chemotherapy treatment side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and reduced immunity can persist for weeks or months, and follow-up visits help doctors manage them properly. Early detection of ongoing symptoms allows timely adjustments in medications or lifestyle recommendations to support recovery.
- Detects long-term organ effects: Chemotherapy may impact organs such as the heart, liver, or kidneys, and these issues can develop silently after treatment has ended. Regular checkups include blood tests and imaging to identify early signs of organ stress before they become severe.
- Addresses chemo side effects on brain function: Cognitive changes, often referred to as “chemo brain,” can include memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and slower thinking. Follow-up care provides strategies and monitoring to help patients manage these chemo side effects on brain functions effectively.
- Prevents recurrence or detects cancer early: Follow-up tests ensure that any signs of cancer returning are identified as early as possible when treatment is more effective. Imaging scans and tumor marker assessments help doctors evaluate progress and catch subtle changes.
- Supports emotional and mental health: Post-treatment anxiety, mood changes, and fear of recurrence are common after chemotherapy. Follow-up visits create a safe space to address these concerns while offering guidance, counseling options, and supportive care.
- Helps manage late-appearing chemotherapy cancer treatment side effects: Some chemotherapy cancer treatment side effects—such as nerve damage, hormonal changes, or reproductive issues—may appear months or years later. Consistent follow-up allows healthcare teams to identify patterns early and provide appropriate interventions.
- Ensures overall rehabilitation and lifestyle support: Follow-up care includes guidance on nutrition, physical activity, and healthy habits that help rebuild strength and immunity. Personalized recovery plans improve long-term health and reduce the risk of future complications.
Conclusion
Chemotherapy is a powerful tool in cancer treatment, but it often comes with side effects that can vary from person to person. During your 1st chemo treatment, you may experience common side effects such as fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and changes in cognitive function, often called “chemo brain.” Understanding these chemotherapy side effects and how to manage them through rest, proper nutrition, and medications can significantly improve your ability to cope during treatment. While these side effects may be challenging, they are a normal part of the process, and your medical team can help you navigate them effectively.
Read Also: Cancer Screening test




